Scoliosis is a condition that causes a person’s spine to curve sideways in an “S” or “C” shape.
It is most commonly found in adolescents but can also affect adults.
It can cause pain and lead to other issues, such as balance and breathing difficulties.
Symptoms of Scoliosis
- Uneven shoulders
- Uneven waist
- One hip higher than the other
- Visible curvature of the spine
- Uneven arms or legs
- One shoulder blade appears more prominent than the other
- Back pain
- Fatigue
- Difficulty breathing
- Poor posture
6 Common Risk factors of Scoliosis
1. Being female – Girls are more likely to develop scoliosis than boys.
2. Family history – Scoliosis tends to run in families.
3. Age – Scoliosis is most commonly diagnosed during the growth spurt that occurs before puberty.
4. Neuromuscular conditions – People with conditions such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy are more likely to develop scoliosis.
5. Birth defects – Defects of the spine, such as spina bifida, can cause scoliosis.
6. Injury – Trauma to the spine can cause scoliosis.
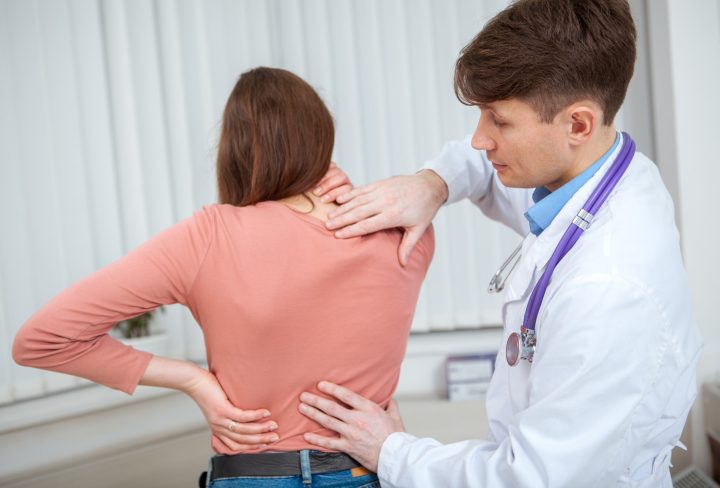
Diagnosis of Scoliosis
Scoliosis is typically diagnosed by a physical exam. The doctor will look for signs of abnormal curvature of the spine, such as one shoulder being higher than the other, a visible curve in the back when the patient bends forward, or a protruding rib cage.
The doctor may also feel along the spine to check for unusual bumps or ridges. X-rays may also be taken to confirm the diagnosis and measure the curvature degree.
Treatment of scoliosis
Treatment for scoliosis depends on the severity of the curve, age, and how quickly the curve is progressing.
- Mild scoliosis often does not require any treatment, but regular monitoring is recommended
- Moderate scoliosis may require bracing or physical therapy to help slow the progression of the curve
- Severe scoliosis may require surgery to correct the curve and prevent further progression
Tips to Deal with Scoliosis
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet: A healthy, balanced diet can help support a healthy spine. Include plenty of fruits and vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. Avoid processed foods and sugary drinks.
2. Exercise Regularly: Regular exercise can help strengthen the core and improve posture, which can help reduce the appearance of scoliosis. Try low-impact activities like swimming, yoga, and biking.
3. Use Proper Posture: Improving posture can help reduce the appearance of scoliosis. Stand up straight and tall; keep your shoulders back and your chin up.
4. Stretch and Strengthen Muscles: Stretching and strengthening the muscles around the spine can help reduce the appearance of scoliosis. Talk to a physical therapist to learn the best stretches and exercises.
5. Wear a Back Brace: A back brace may be recommended for severe cases of scoliosis. This helps reduce the curvature of the spine and prevent further worsening.
6. Get Regular Check-Ups: Regular check-ups with your doctor can help monitor the progression of scoliosis. Your doctor may suggest further treatments if the curvature of the spine wors
Myth and Fact on Scoliosis
Myth: Scoliosis is a sign of bad posture.
Fact: Scoliosis is a curvature of the spine not caused by poor posture. It is a genetic condition that can affect people of any age, although it is most common in adolescents.
FAQs on Scoliosis
What are the surgical procedures for scoliosis?
Several surgical procedures can be used to treat scoliosis; the most common are:
- Spinal fusion
- Vertebral column resection (VCR)
- Hemivertebra Resection
- Growing Rod
It’s important to note that surgery is usually only recommended for severe cases of scoliosis and when the curve is causing significant pain, difficulty breathing, or when the curve is progressing rapidly.
Each case of scoliosis is different, and the surgical approach will be tailored to the individual patient’s needs and preferences.